

Writing the best nursing care plan requires a step-by-step approach to complete the parts needed for a care plan correctly. This tutorial will walk you through developing a care plan. This guide has the ultimate database and list of nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnosis samples for our student nurses and professional nurses to use—all for free! Care plan components, examples, objectives, and purposes are included with a detailed guide on writing an excellent nursing care plan or a template for your unit.
A nursing care plan (NCP) is a formal process that correctly identifies existing needs and recognizes a client’s potential needs or risks. Care plans provide a way of communication among nurses, their patients, and other healthcare providers to achieve healthcare outcomes. Without the nursing care planning process, the quality and consistency of patient care would be lost.
Nursing care planning begins when the client is admitted to the agency and is continuously updated throughout in response to the client’s changes in condition and evaluation of goal achievement. Planning and delivering individualized or patient-centered care is the basis for excellence in nursing practice.
Care plans can be informal or formal: An informal nursing care plan is a strategy of action that exists in the nurse‘s mind. A formal nursing care plan is a written or computerized guide that organizes the client’s care information.
Formal care plans are further subdivided into standardized care plans and individualized care plans: Standardized care plans specify the nursing care for groups of clients with everyday needs. Individualized care plans are tailored to meet a specific client’s unique needs or needs that are not addressed by the standardized care plan.
Standardized care plans are pre-developed guides by the nursing staff and health care agencies to ensure that patients with a particular condition receive consistent care. These care plans are used to ensure that minimally acceptable criteria are met and to promote the efficient use of the nurse’s time by removing the need to develop common activities that are done repeatedly for many of the clients on a nursing unit.
Standardized care plans are not tailored to a patient’s specific needs and goals and can provide a starting point for developing an individualized care plan.
Care plans listed in this guide are standard care plans which can serve as a framework or direction to develop an individualized care plan.
An individualized care plan care plan involves tailoring a standardized care plan to meet the specific needs and goals of the individual client and use approaches shown to be effective for a particular client. This approach allows more personalized and holistic care better suited to the client’s unique needs, strengths, and goals.
Additionally, individualized care plans can improve patient satisfaction. When patients feel that their care is tailored to their specific needs, they are more likely to feel heard and valued, leading to increased satisfaction with their care. This is particularly important in today’s healthcare environment, where patient satisfaction is increasingly used as a quality measure.
Tips on how to individualize a nursing care plan:
The following are the goals and objectives of writing a nursing care plan:
The following are the purposes and importance of writing a nursing care plan:
A nursing care plan (NCP) usually includes nursing diagnoses, client problems, expected outcomes, nursing interventions, and rationales. These components are elaborated on below:
Nursing care plan formats are usually categorized or organized into four columns: (1) nursing diagnoses, (2) desired outcomes and goals, (3) nursing interventions, and (4) evaluation. Some agencies use a three-column plan where goals and evaluation are in the same column. Other agencies have a five-column plan that includes a column for assessment cues.
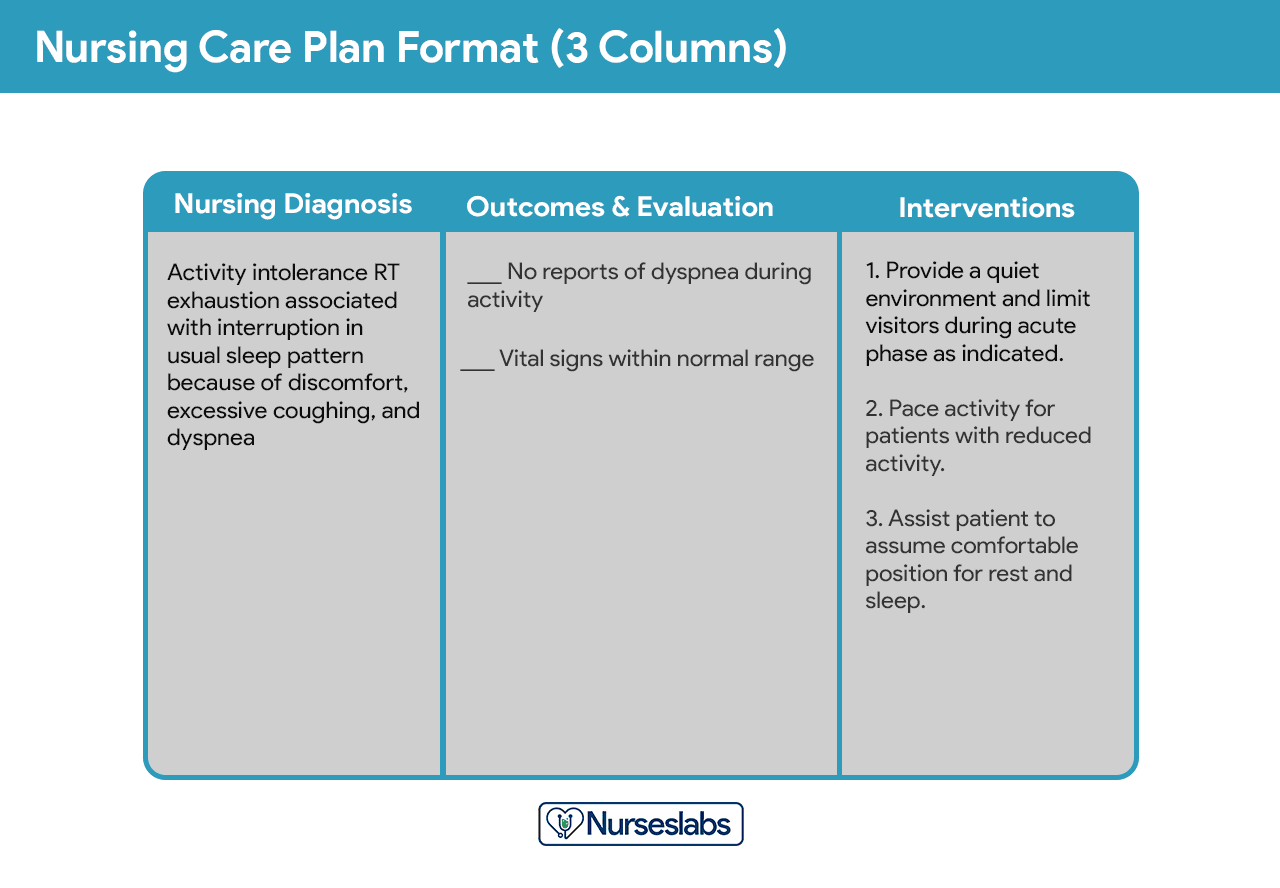
The three-column plan has a column for nursing diagnosis, outcomes and evaluation, and interventions.
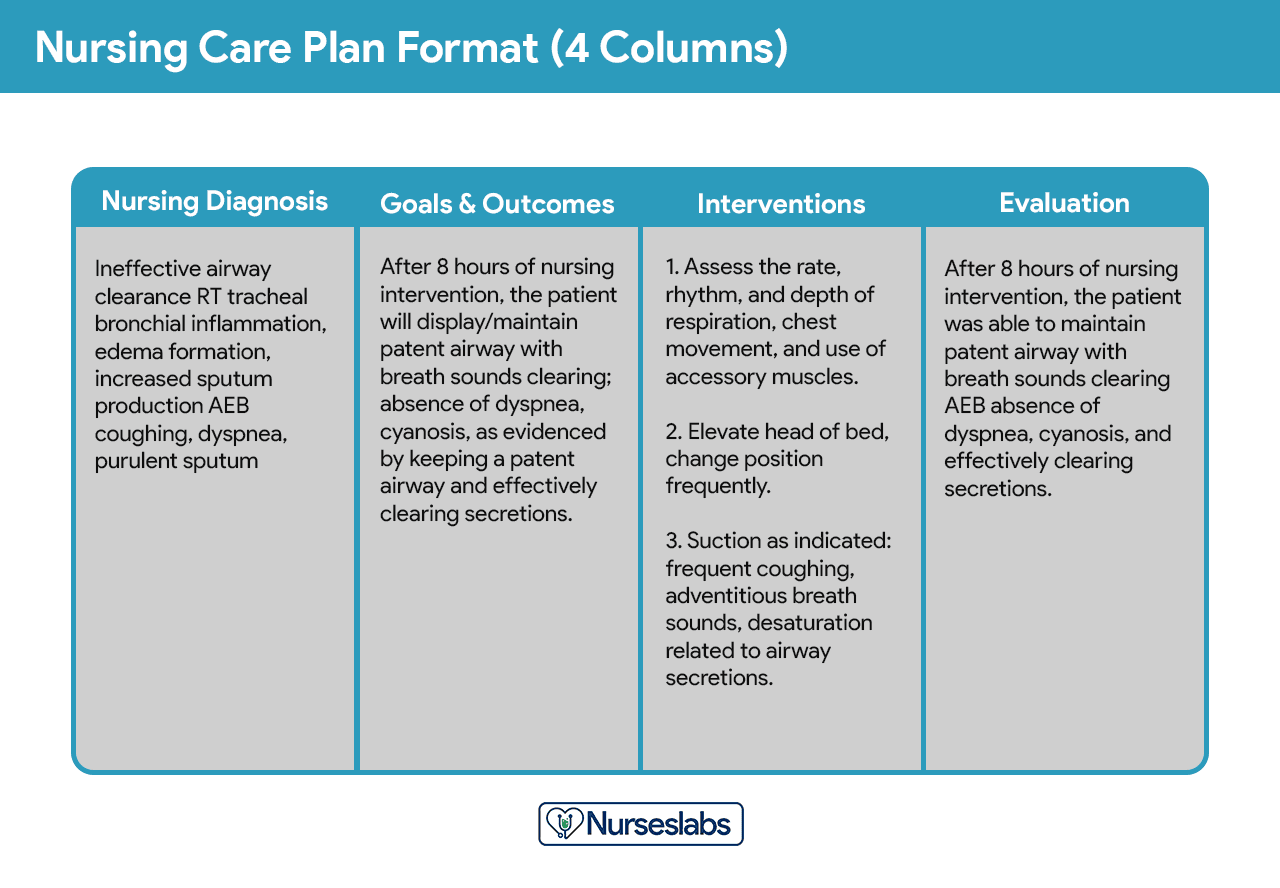
This format includes columns for nursing diagnosis, goals and outcomes, interventions, and evaluation.
Below is a document containing sample templates for the different nursing care plan formats. Please feel free to edit, modify, and share the template.
Student care plans are more lengthy and detailed than care plans used by working nurses because they serve as a learning activity for the student nurse.
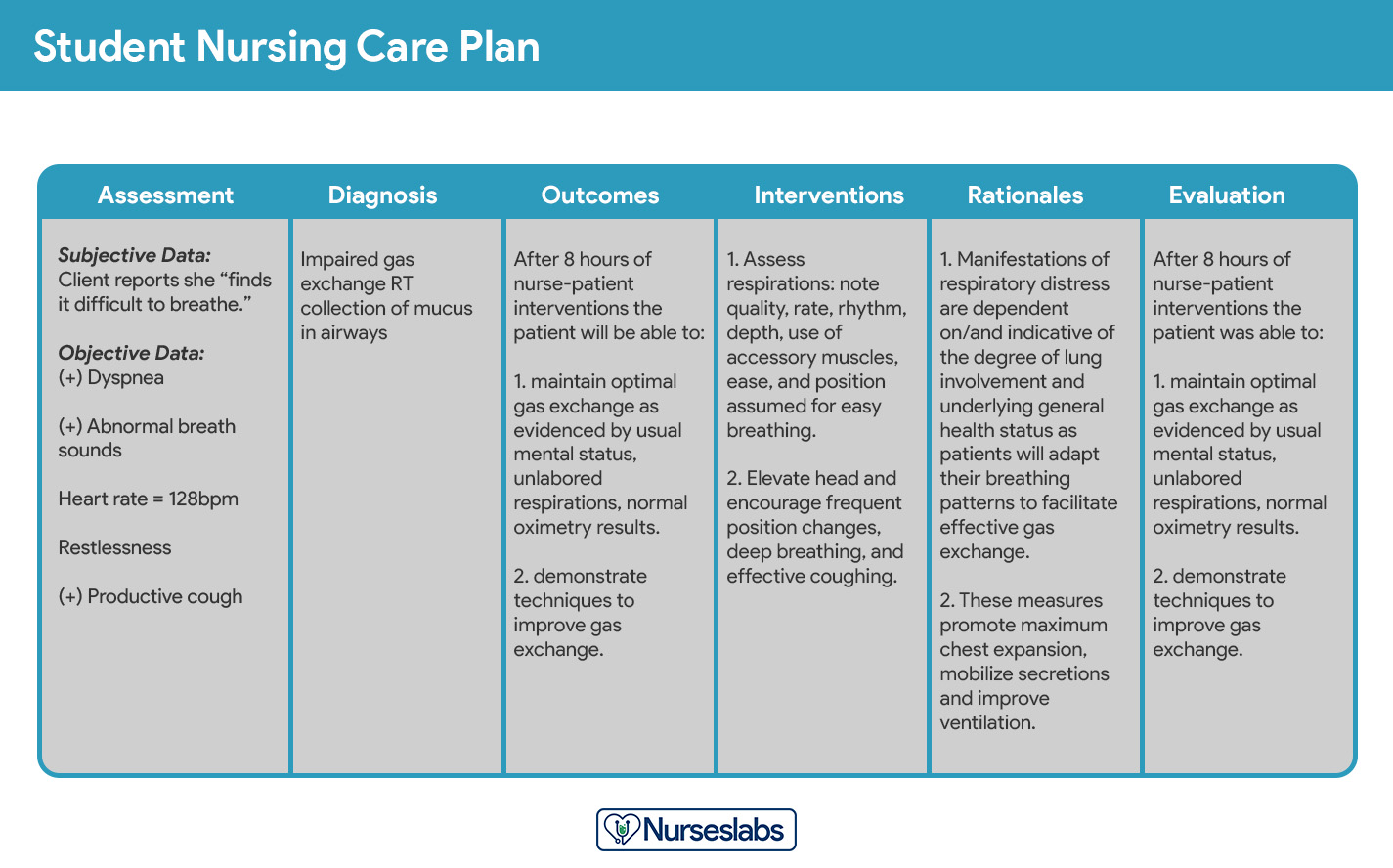
Care plans by student nurses are usually required to be handwritten and have an additional column for “Rationale” or “Scientific Explanation” after the nursing interventions column. Rationales are scientific principles that explain the reasons for selecting a particular nursing intervention.
How do you write a nursing care plan (NCP)? Just follow the steps below to develop a care plan for your client.
The first step in writing a nursing care plan is to create a client database using assessment techniques and data collection methods (physical assessment, health history, interview, medical records review, and diagnostic studies). A client database includes all the health information gathered. In this step, the nurse can identify the related or risk factors and defining characteristics that can be used to formulate a nursing diagnosis. Some agencies or nursing schools have specific assessment formats you can use.
Critical thinking is key in patient assessment, integrating knowledge across sciences and professional guidelines to inform evaluations. This process, crucial for complex clinical decision-making, aims to identify patients’ healthcare needs effectively, leveraging a supportive environment and reliable information
Now that you have information about the client’s health, analyze, cluster, and organize the data to formulate your nursing diagnosis, priorities, and desired outcomes.
Nursing diagnoses are a uniform way of identifying, focusing on and dealing with specific client needs and responses to actual and high-risk problems. Actual or potential health problems that can be prevented or resolved by independent nursing intervention are termed nursing diagnoses.
We’ve detailed the steps on how to formulate your nursing diagnoses in this guide: Nursing Diagnosis (NDx): Complete Guide and List.
Setting priorities involves establishing a preferential sequence for addressing nursing diagnoses and interventions. In this step, the nurse and the client begin planning which of the identified problems requires attention first. Diagnoses can be ranked and grouped as having a high, medium, or low priority. Life-threatening problems should be given high priority.
A nursing diagnosis encompasses Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and helps to prioritize and plan care based on patient-centered outcomes. In 1943, Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchy based on basic fundamental needs innate to all individuals. Basic physiological needs/goals must be met before higher needs/goals can be achieved, such as self-esteem and self-actualization. Physiological and safety needs are the basis for implementing nursing care and interventions. Thus, they are at the base of Maslow’s pyramid, laying the foundation for physical and emotional health.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
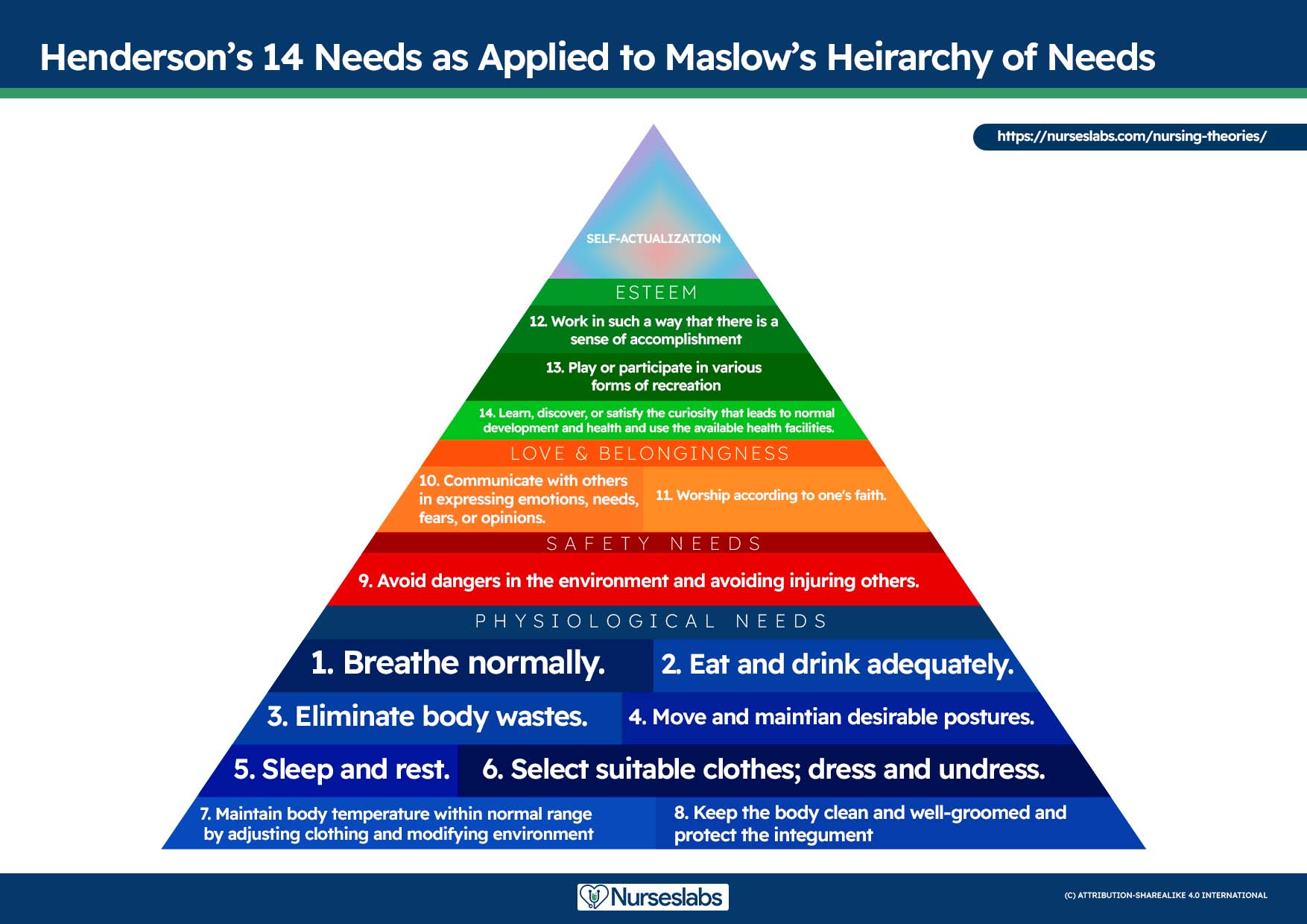
The client’s health values and beliefs, priorities, resources available, and urgency are factors the nurse must consider when assigning priorities. Involve the client in the process to enhance cooperation.
After assigning priorities for your nursing diagnosis, the nurse and the client set goals for each determined priority. Goals or desired outcomes describe what the nurse hopes to achieve by implementing the nursing interventions derived from the client’s nursing diagnoses. Goals provide direction for planning interventions, serve as criteria for evaluating client progress, enable the client and nurse to determine which problems have been resolved, and help motivate the client and nurse by providing a sense of achievement.
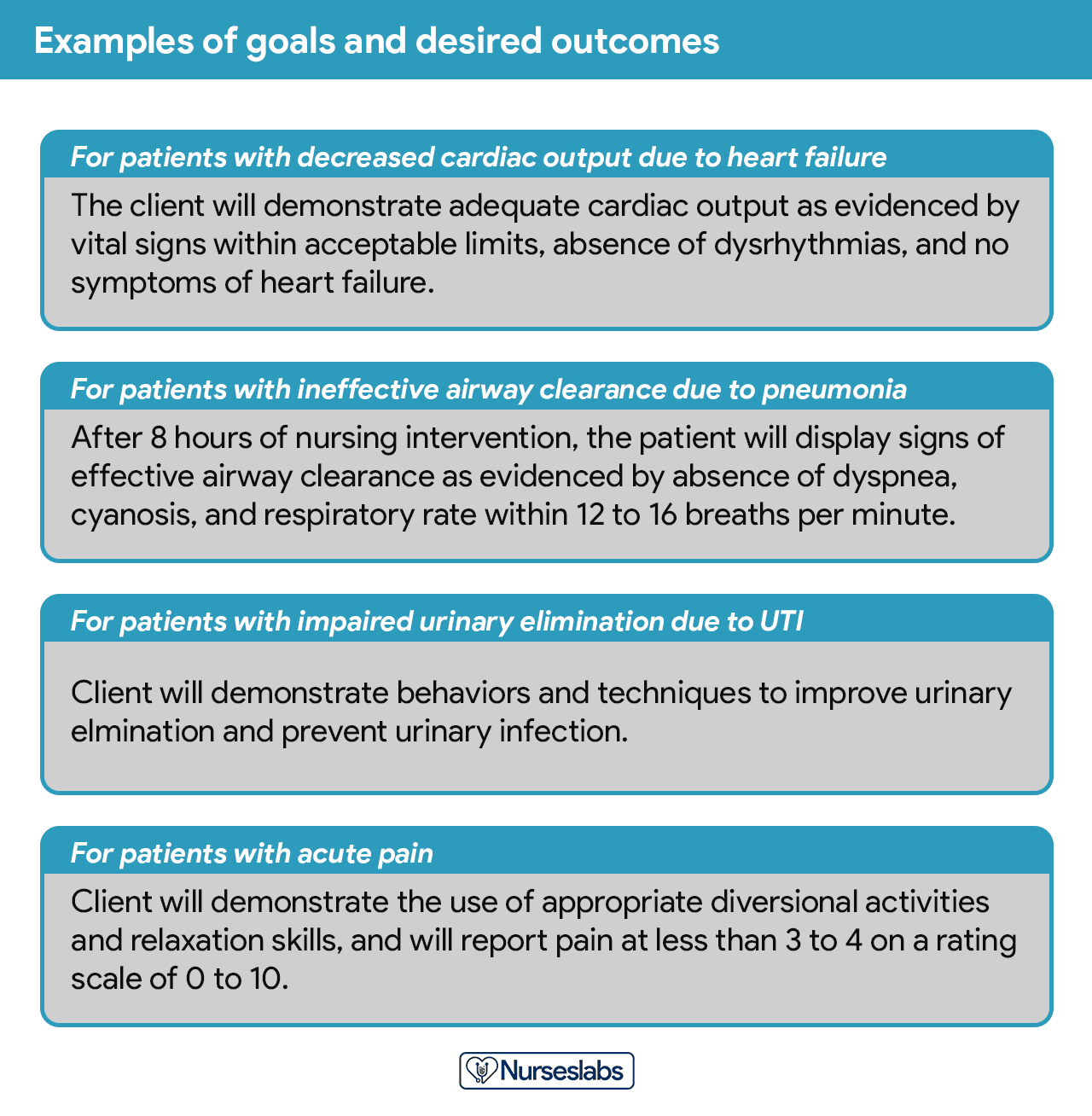
One overall goal is determined for each nursing diagnosis. The terms “goal outcomes“ and “expected outcomes” are often used interchangeably.
According to Hamilton and Price (2013), goals should be SMART. SMART stands for specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-oriented goals.
Hogston (2011) suggests using the REEPIG standards to ensure that care is of the highest standards. By this means, nursing care plans should be:
Goals and expected outcomes must be measurable and client-centered. Goals are constructed by focusing on problem prevention, resolution, and rehabilitation. Goals can be short-term or long-term. Most goals are short-term in an acute care setting since much of the nurse’s time is spent on the client’s immediate needs. Long-term goals are often used for clients who have chronic health problems or live at home, in nursing homes, or in extended-care facilities.
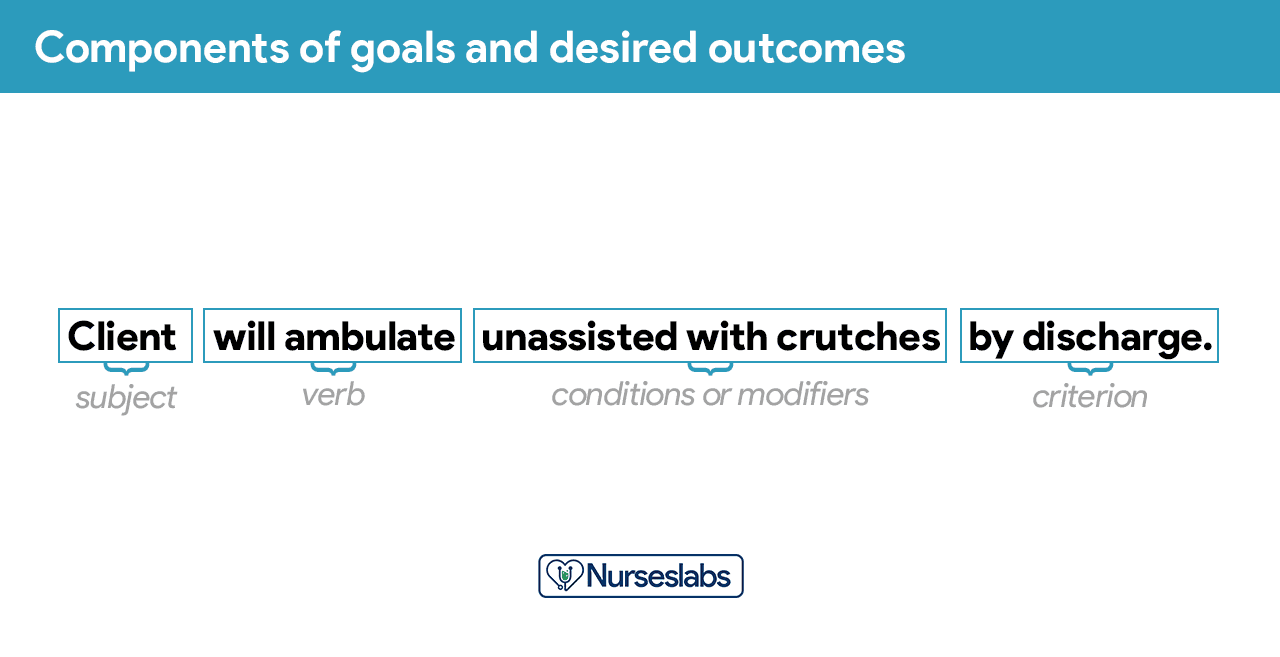
Goals or desired outcome statements usually have four components: a subject, a verb, conditions or modifiers, and a criterion of desired performance.
When writing goals and desired outcomes, the nurse should follow these tips:
Nursing interventions are activities or actions that a nurse performs to achieve client goals. Interventions chosen should focus on eliminating or reducing the etiology of the priority nursing problem or diagnosis. As for risk nursing problems, interventions should focus on reducing the client’s risk factors. In this step, nursing interventions are identified and written during the planning step of the nursing process; however, they are actually performed during the implementation step.
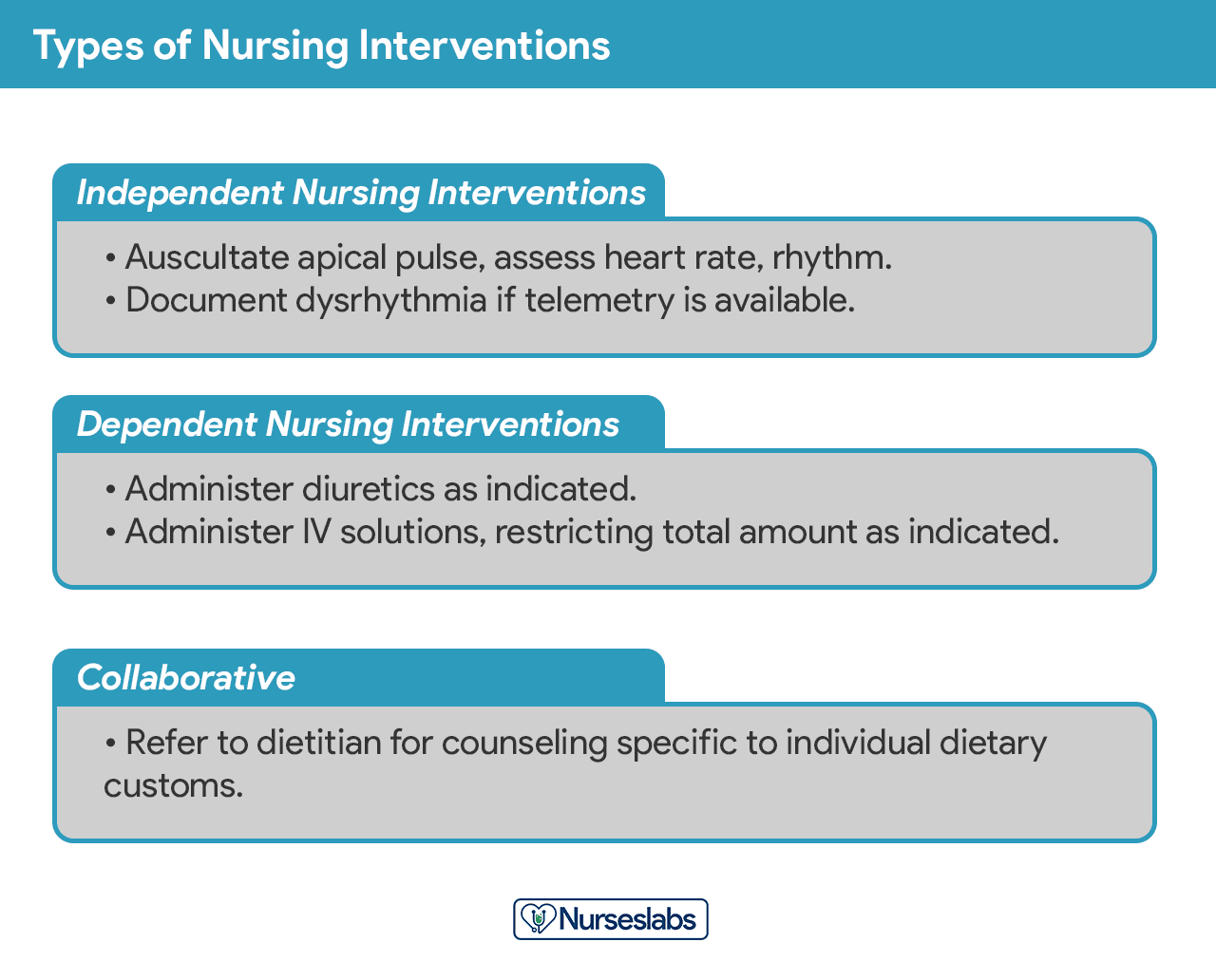
Nursing interventions can be independent, dependent, or collaborative:
When writing nursing interventions, follow these tips:
Rationales, also known as scientific explanations, explain why the nursing intervention was chosen for the NCP.
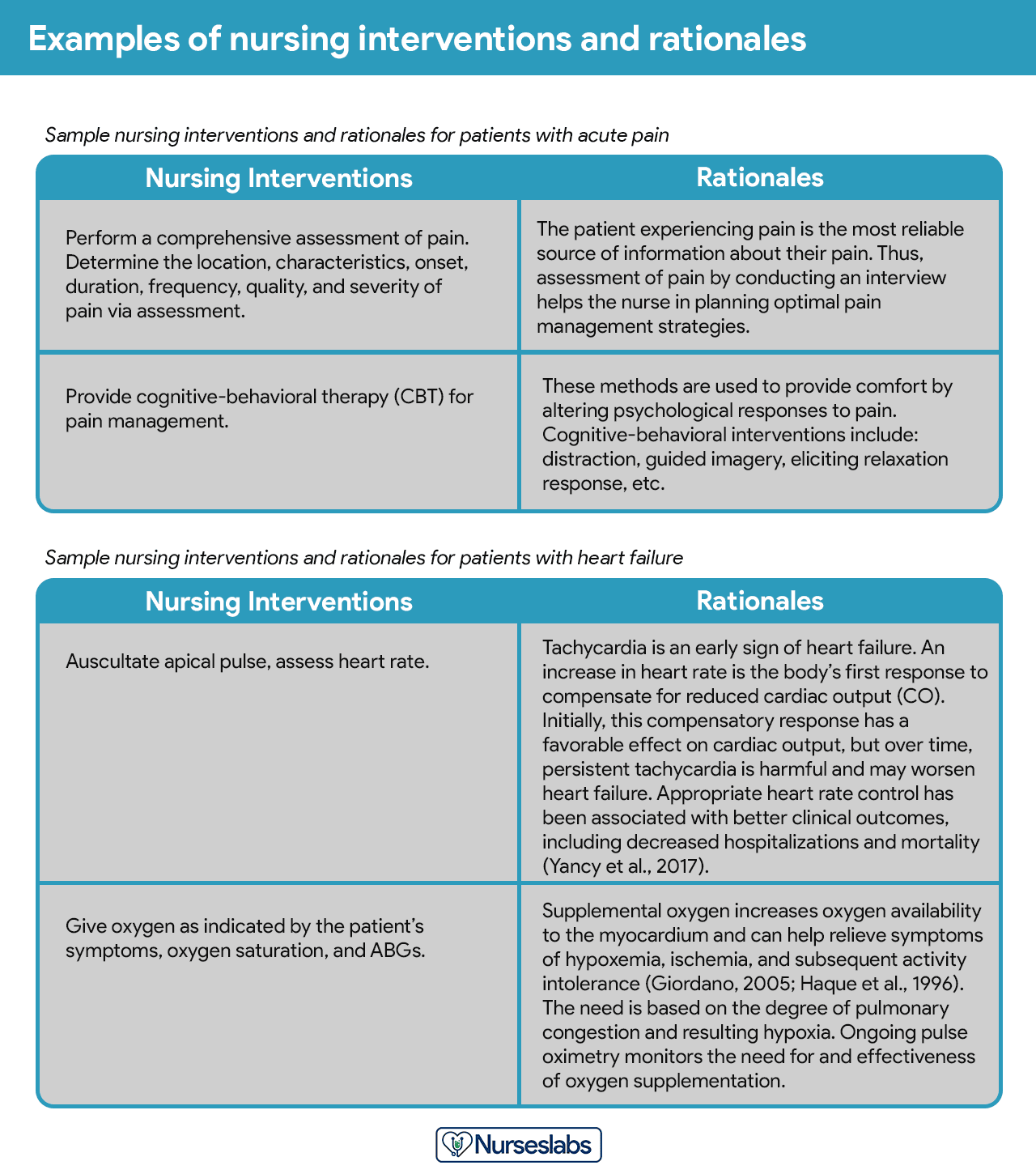
Rationales do not appear in regular care plans. They are included to assist nursing students in associating the pathophysiological and psychological principles with the selected nursing intervention.
Evaluation is a planned, ongoing, purposeful activity in which the client’s progress towards achieving goals or desired outcomes is assessed, and the effectiveness of the nursing care plan (NCP). Evaluation is an essential aspect of the nursing process because the conclusions drawn from this step determine whether the nursing intervention should be terminated, continued, or changed.
The client’s care plan is documented according to hospital policy and becomes part of the client’s permanent medical record, which may be reviewed by the oncoming nurse. Different nursing programs have different care plan formats. Most are designed so that the student systematically proceeds through the interrelated steps of the nursing process, and many use a five-column format.
This section lists the sample nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnoses for various diseases and health conditions. They are segmented into categories:
Miscellaneous nursing care plans examples that don’t fit other categories:
| Basic Nursing & General Care Plans |
|---|
| Acute Confusion (Delirium) and Altered Mental Status |
| Acute Pain and Pain Management |
| Activity Intolerance and Generalized Weakness |
| Cancer (Oncology Nursing) |
| Caregiver Role Strain and Family Caregiver Support Systems |
| Chronic Confusion (Dementia) |
| End-of-Life Care (Hospice Care or Palliative) |
| Fall Risk and Fall Prevention |
| Fatigue and Lethargy |
| Geriatric Nursing (Older Adult) |
| Grieving and Loss |
| Hypothermia and Cold Injuries |
| Hyperthermia (Fever) |
| Impaired Swallowing (Dysphagia) |
| Insomnia and Sleep Deprivation |
| Prolonged Bed Rest |
| Risk for Injury and Patient Safety |
| Self-Care and Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) |
| Surgery (Perioperative Client) |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| Total Parenteral Nutrition |
| Surgery and Perioperative Care Plans |
|---|
| Amputation |
| Appendectomy |
| Cholecystectomy |
| Fracture UPDATED! |
| Hemorrhoids |
| Hysterectomy |
| Ileostomy & Colostomy |
| Laminectomy (Disc Surgery) |
| Mastectomy |
| Subtotal Gastrectomy |
| Surgery (Perioperative Client) |
| Thyroidectomy |
| Total Joint (Knee, Hip) Replacement |
Nursing care plans about the different diseases of the cardiovascular system:
| Cardiac Care Plans |
|---|
| Angina Pectoris (Coronary Artery Disease) |
| Cardiac Arrhythmia (Digitalis Toxicity) |
| Cardiac Catheterization |
| Cardiogenic Shock |
| Congenital Heart Disease |
| Decreased Cardiac Output & Cardiac Support |
| Heart Failure UPDATED! |
| Hypertension UPDATED! |
| Hypovolemic Shock |
| Impaired Tissue Perfusion & Ischemia |
| Myocardial Infarction |
| Pacemaker Therapy |
Nursing care plans (NCP) related to the endocrine system and metabolism:
| Endocrine and Metabolic Care Plans |
|---|
| Addison’s Disease |
| Cushing’s Disease |
| Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1, Type 2) UPDATED! |
| Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS) |
| Eating Disorders: Anorexia & Bulimia Nervosa |
| Fluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration & Hypovolemia) |
| Fluid Volume Excess (Hypervolemia) |
| Gestational Diabetes Mellitus |
| Hyperthyroidism |
| Hypothyroidism |
| Imbalanced Nutrition (Malnutrition) |
| Obesity & Overweight |
| Thyroidectomy |
| Unstable Blood Glucose Levels (Hyperglycemia & Hypoglycemia) |
| Acid-Base Imbalances |
|---|
| Metabolic Acidosis |
| Metabolic Alkalosis |
| Respiratory Acidosis |
| Respiratory Alkalosis |
| Electrolyte Imbalances |
|---|
| Calcium (Ca) Imbalances: Hypercalcemia and Hypocalcemia |
| Magnesium (Mg) Imbalances: Hypermagnesemia and Hypomagnesemia |
| Potassium (K) Imbalances: Hyperkalemia and Hypokalemia |
| Sodium (Na) Imbalances: Hypernatremia and Hyponatremia |
Care plans (NCP) covering the disorders of the gastrointestinal and digestive system:
| Gastrointestinal Care Plans |
|---|
| Appendectomy |
| Bowel Incontinence (Fecal Incontinence) |
| Cholecystectomy |
| Constipation |
| Diarrhea Nursing Care Plan and Management |
| Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis |
| Gastroenteritis |
| Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) |
| Hemorrhoids |
| Hepatitis |
| Ileostomy & Colostomy |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) |
| Intussusception |
| Liver Cirrhosis |
| Nausea & Vomiting |
| Pancreatitis |
| Peritonitis |
| Peptic Ulcer Disease |
| Subtotal Gastrectomy |
| Umbilical and Inguinal Hernia |
Care plans related to the hematologic and lymphatic system:
| Hematologic & Lymphatic Care Plans |
|---|
| Anaphylactic Shock |
| Anemia UPDATED! |
| Aortic Aneurysm |
| Bleeding Risk & Hemophilia |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation |
| Hemophilia |
| Kawasaki Disease |
| Leukemia |
| Lymphoma |
| Sepsis and Septicemia |
| Sickle Cell Anemia Crisis |
NCPs for communicable and infectious diseases:
| Infectious Diseases Care Plans |
|---|
| Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) (HIV Positive) |
| Acute Rheumatic Fever |
| Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever |
| Herpes Zoster (Shingles) |
| Influenza (Flu) |
| Pulmonary Tuberculosis |
| Risk for Infection & Infection Control |
All about disorders and conditions affecting the integumentary system:
| Integumentary Care Plans |
|---|
| Burn Injury |
| Dermatitis |
| Herpes Zoster (Shingles) |
| Pressure Ulcer (Bedsores) |
| Wound Care and Skin/Tissue Integrity |
Nursing care plans about the care of the pregnant mother and her infant. See care plans for maternity and obstetric nursing:
| Maternal and Newborn Care Plans |
|---|
| Abortion (Termination of Pregnancy) |
| Cervical Insufficiency (Premature Dilation of the Cervix) |
| Cesarean Birth |
| Cleft Palate and Cleft Lip |
| Gestational Diabetes Mellitus |
| Hyperbilirubinemia (Jaundice) |
| Labor Stages, Induced, Augmented, Dysfunctional, Precipitous Labor |
| Neonatal Sepsis |
| Perinatal Loss (Miscarriage, Stillbirth) |
| Placental Abruption |
| Placenta Previa |
| Postpartum Hemorrhage |
| Postpartum Thrombophlebitis |
| Prenatal Hemorrhage |
| Preeclampsia and Gestational Hypertension |
| Prenatal Infection |
| Preterm Labor |
| Puerperal & Postpartum Infections |
| Substance (Alcohol and Drug) Abuse in Pregnancy |
Care plans for mental health and psychiatric nursing:
| Mental Health and Psychiatric Care Plans |
|---|
| Alcohol Withdrawal |
| Anxiety & Fear |
| Anxiety and Panic Disorders |
| Bipolar Disorders |
| Body Image Disturbance & Self-Esteem |
| Impaired Thought Processes & Cognitive Impairment |
| Major Depression |
| Personality Disorders |
| Schizophrenia |
| Sexual Assault |
| Substance Dependence and Abuse |
| Suicide Behaviors |
Care plans related to the musculoskeletal system:
| Musculoskeletal Care Plans |
|---|
| Amputation |
| Congenital Hip Dysplasia |
| Fracture UPDATED! |
| Impaired Physical Mobility & Immobility |
| Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Laminectomy (Disc Surgery) |
| Osteoarthritis |
| Osteogenic Sarcoma (Osteosarcoma) |
| Osteoporosis |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Scoliosis |
| Spinal Cord Injury |
| Total Joint (Knee, Hip) Replacement |
Nursing care plans (NCP) for related to nervous system disorders:
| Neurological Care Plans |
|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease UPDATED! |
| Brain Tumor |
| Cerebral Palsy |
| Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) UPDATED! |
| Guillain-Barre Syndrome |
| Meningitis |
| Multiple Sclerosis |
| Parkinson’s Disease |
| Seizure Disorder |
| Spinal Cord Injury |
Care plans relating to eye disorders:
| Ophthalmic Care Plans |
|---|
| Cataracts |
| Glaucoma |
| Macular Degeneration |
Nursing care plans (NCP) for pediatric conditions and diseases:
| Pediatric Nursing Care Plans |
|---|
| Child Abuse |
| Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate |
| Dying Child |
| Febrile Seizure |
| Hospitalized Child |
| Hydrocephalus |
| Otitis Media |
| Spina Bifida |
| Tonsillitis and Adenoiditis |
Care plans related to the reproductive and sexual function disorders:
| Reproductive Care Plans |
|---|
| Cryptorchidism (Undescended Testes) |
| Hysterectomy |
| Hypospadias and Epispadias |
| Mastectomy |
| Menopause |
| Prostatectomy |
Care plans for respiratory system disorders:
| Respiratory Care Plans |
|---|
| Airway Clearance Therapy & Coughing |
| Apnea |
| Asthma UPDATED! |
| Aspiration Risk & Aspiration Pneumonia |
| Bronchiolitis UPDATED! |
| Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) UPDATED! |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) UPDATED! |
| Croup Syndrome |
| Cystic Fibrosis UPDATED! |
| Epiglottitis |
| Hemothorax and Pneumothorax UPDATED! |
| Ineffective Breathing Pattern (Dyspnea) |
| Impairment of Gas Exchange |
| Influenza (Flu) UPDATED! |
| Lung Cancer UPDATED! |
| Mechanical Ventilation |
| Near-Drowning |
| Pleural Effusion |
| Pneumonia |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Pulmonary Tuberculosis |
| Tracheostomy |
Care plans related to the kidney and urinary system disorders:
| Urinary Care Plans |
|---|
| Acute Glomerulonephritis |
| Acute Renal Failure |
| Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) |
| Chronic Renal Failure |
| Hemodialysis |
| Nephrotic Syndrome |
| Peritoneal Dialysis |
| Urolithiasis (Renal Calculi) |
| Urinary Elimination (Urinary Incontinence & Urinary Retention) |
| Urinary Tract Infection |
| Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) |
| Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma) |
Recommended nursing diagnosis and nursing care plan books and resources.
Disclosure: Included below are affiliate links from Amazon at no additional cost from you. We may earn a small commission from your purchase. For more information, check out our privacy policy.
Ackley and Ladwig’s Nursing Diagnosis Handbook: An Evidence-Based Guide to Planning Care
We love this book because of its evidence-based approach to nursing interventions. This care plan handbook uses an easy, three-step system to guide you through client assessment, nursing diagnosis, and care planning. Includes step-by-step instructions showing how to implement care and evaluate outcomes, and help you build skills in diagnostic reasoning and critical thinking.

Nursing Care Plans – Nursing Diagnosis & Intervention (10th Edition)
Includes over two hundred care plans that reflect the most recent evidence-based guidelines. New to this edition are ICNP diagnoses, care plans on LGBTQ health issues, and on electrolytes and acid-base balance.

Nurse’s Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions, and Rationales
Quick-reference tool includes all you need to identify the correct diagnoses for efficient patient care planning. The sixteenth edition includes the most recent nursing diagnoses and interventions and an alphabetized listing of nursing diagnoses covering more than 400 disorders.

Nursing Diagnosis Manual: Planning, Individualizing, and Documenting Client Care
Identify interventions to plan, individualize, and document care for more than 800 diseases and disorders. Only in the Nursing Diagnosis Manual will you find for each diagnosis subjectively and objectively – sample clinical applications, prioritized action/interventions with rationales – a documentation section, and much more!

All-in-One Nursing Care Planning Resource – E-Book: Medical-Surgical, Pediatric, Maternity, and Psychiatric-Mental Health
Includes over 100 care plans for medical-surgical, maternity/OB, pediatrics, and psychiatric and mental health. Interprofessional “patient problems” focus familiarizes you with how to speak to patients.

Recommended reading materials and sources for this NCP guide:
Matt Vera, a registered nurse since 2009, leverages his experiences as a former student struggling with complex nursing topics to help aspiring nurses as a full-time writer and editor for Nurseslabs, simplifying the learning process, breaking down complicated subjects, and finding innovative ways to assist students in reaching their full potential as future healthcare providers.